When we talk about the backbone materials of modern industry, there is a special alloy quietly supporting our world. It forms the teeth of excavators that bite into rock, the hammers of crushers that pulverize ore, the track links of tanks that resist wear, and even the inner layers of safes that protect our security. This material is manganese steel, and the process of shaping it into various complex forms is manganese steel casting. This article will take you from scratch to a comprehensive understanding of this magical process and material. (Learn more about what metal casting is)
1. What is Manganese Steel? Why is it so Special?
Manganese steel, accurately called "high manganese steel," is an iron-based alloy containing 11-14% manganese and about 1% carbon. This seemingly simple recipe creates a material with peculiar properties. Its most famous grade is Hadfield steel (named after British metallurgist Robert Hadfield), which has remained largely unchanged since its invention in 1882, yet remains enduringly popular.
To understand what makes manganese steel special, we need to uncover its microscopic secrets (for readers comparing materials, see cast steel vs forged steel):
- Stable Austenitic Structure: Most steels have a "pearlitic" or "martensitic" structure at room temperature, which is hard but brittle. The addition of manganese allows the steel to maintain an "austenitic" structure at room temperature—this is a face-centered cubic lattice that is tough and ductile, capable of absorbing a large amount of impact energy without fracturing.
- Magical "Work Hardening": This is the most extraordinary property of manganese steel. When its surface is subjected to strong impact or compression, instead of being worn or shattered like ordinary steel, it undergoes "work hardening"—the hardness of the impacted area can increase dramatically from the original HB200 (Brinell hardness) to over HB500, up to a maximum of HB700! The hardened layer can be several millimeters deep. The unimpacted parts remain as tough as before.
Imagine manganese steel as a "self-healing" metal warrior. Normally, it is soft and elastic, able to withstand deformation without breaking (good toughness). But when an enemy (impact, wear) attacks it, the attacked area immediately "arms itself," becoming extremely hard to resist the attack. The more fierce the attack, the harder it becomes! Meanwhile, other unattacked areas remain flexible, preventing overall brittle fracture.
This characteristic makes manganese steel unparalleled in harsh working conditions with high impact and high wear. It may not be the hardest initially, but in use, it becomes increasingly hard, with a lifespan far exceeding that of many materials with higher initial hardness.
2. Complete Process Analysis of Manganese Steel Casting
Manganese steel casting is a high-temperature, high-control manufacturing process. From design to final delivery, each step directly affects toughness, wear resistance, and service life. Below is a simplified step-by-step overview.(You may also reference a general steel casting process overview.)
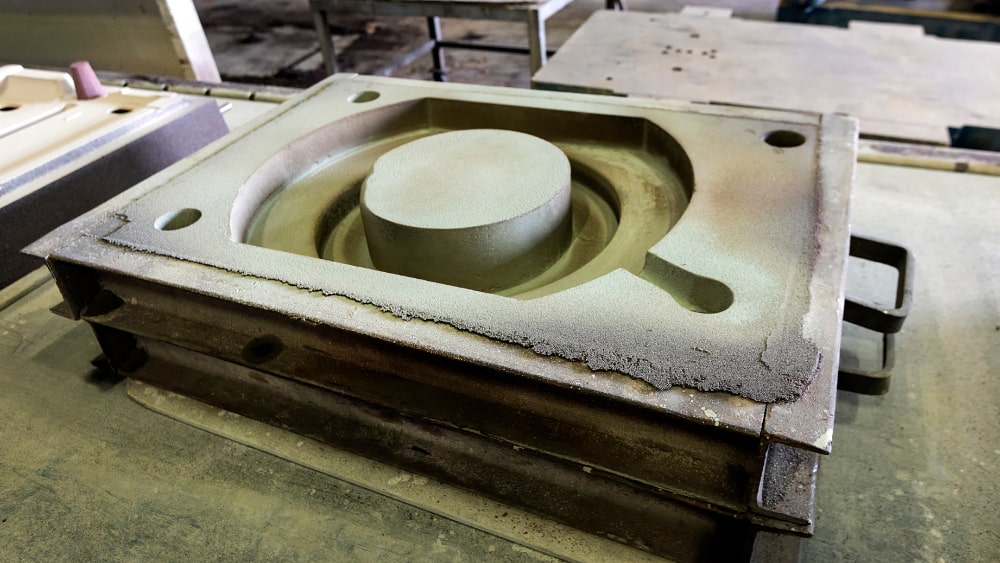
Step 1: Design and Mold Preparation
The process starts with pattern design based on part drawings, allowing for solidification shrinkage. Sand molds and cores are prepared to form the casting shape and internal structures. Because manganese steel is poured at extremely high temperatures (about 1420–1500°C), the mold must have high heat resistance and good gas permeability.
Step 2: Melting and Alloying
Steel scrap, pig iron, and ferromanganese alloys are melted in a medium-frequency induction furnace. Carbon and manganese contents are strictly controlled, and manganese is added at the final stage to reduce oxidation loss. Deoxidation and purification are performed to minimize gas and inclusions.
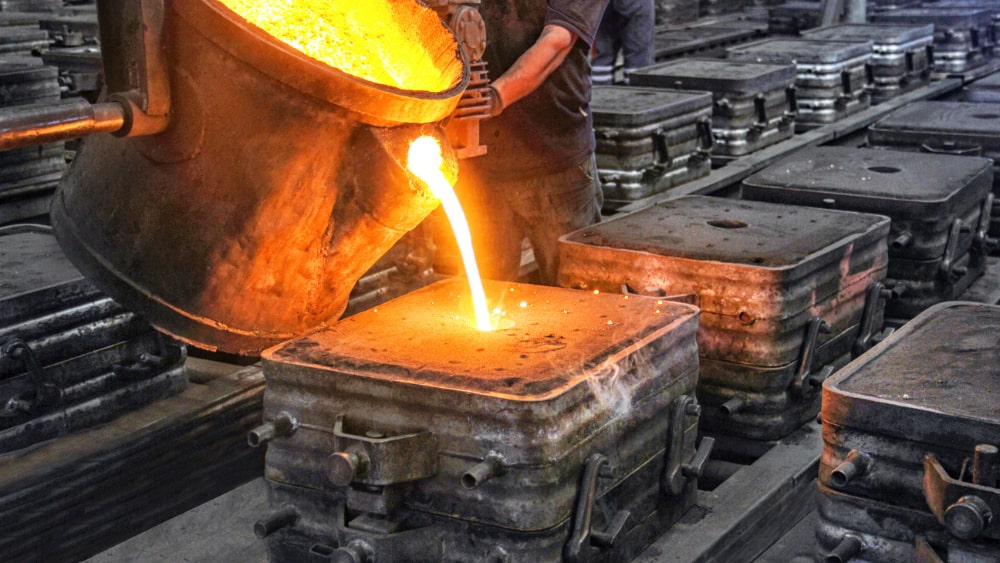
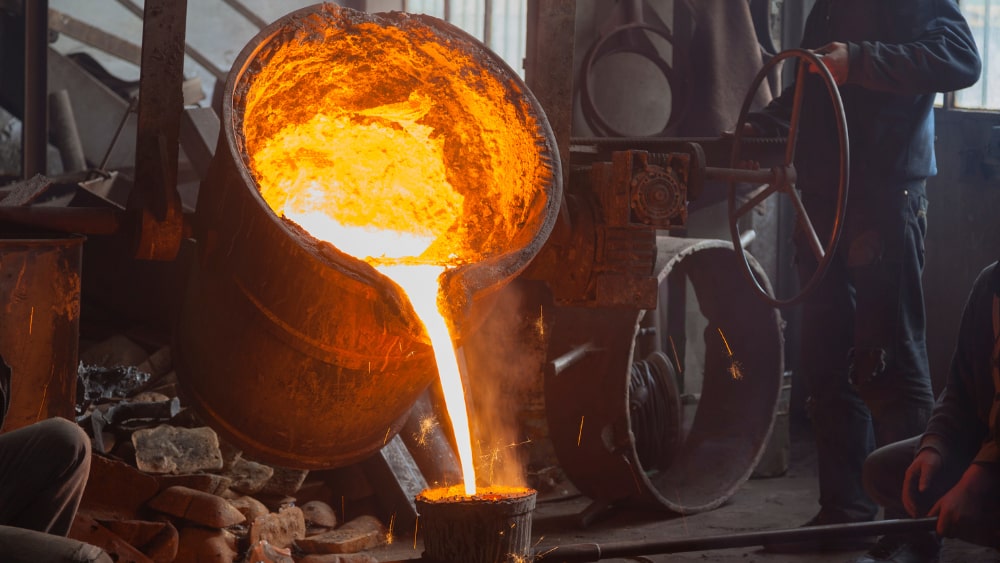
Step 3: Pouring
Molten steel is poured into the mold at a controlled temperature (around 1480°C). Proper pouring speed and temperature are critical to ensure good fluidity, avoid cold shuts, and prevent oxidation or air entrapment.
Step 4: Solidification and Cooling
The molten steel solidifies from the outside inward. Due to high shrinkage, risers and chills are used to prevent shrinkage cavities and porosity. The casting is removed from the mold while still hot, avoiding full cooling to room temperature.
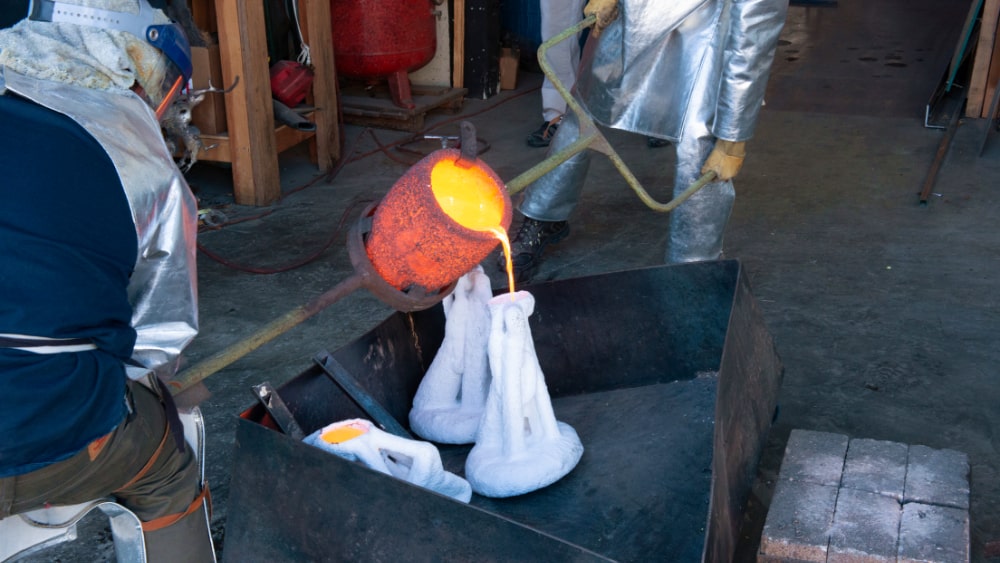
Step 5: Water Toughening Heat Treatment
The casting is heated to 1050–1100°C to fully dissolve carbides, then rapidly quenched in water. This “water toughening” locks in a fully austenitic structure, giving manganese steel its exceptional toughness and work-hardening capability.
Step 6: Cleaning, Inspection, and Delivery
After removing gates and risers, the surface is cleaned by shot blasting. Dimensional checks and non-destructive testing are performed before delivery. The final casting is relatively soft and achieves maximum hardness only during actual impact and wear in service.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Manganese Steel Casting
Advantages:
Extremely high work hardening capacity: Hardness can increase 2-3 times during use, with extremely high surface hardness while the interior remains tough.
Outstanding impact toughness: Can withstand strong impact without fracturing, ensuring safety and reliability.
Good ductility: Can withstand certain plastic deformation in its initial state.
Certain "self-repair" ability: After being impacted and hardened, if the hardened layer is worn away, the underlying layer will continue to harden.
Non-magnetic: The austenitic structure makes it non-magnetic, suitable for special applications.
Limitations:
Low initial hardness: Before work hardening, it is easily scratched by sharp objects.
Relatively low yield strength: Under static loads in the unhardened state, it is prone to deformation.
Difficult to machine: Extremely difficult to cut after hardening, usually only grinding can be performed.
Heat sensitive: Welding or improper heating will cause carbide precipitation, severely damaging properties, requiring special welding procedures.
High casting process requirements: Prone to casting defects, requiring strict process control.
4. Common Applications of Manganese Steel Castings
| Industry/Sector | Specific Components |
|---|---|
| Mining & Quarrying | Crusher jaws, cone crusher liners, hammer mill hammers, ball mill liners, shovel teeth, dredger buckets |
| Railway Transportation | Railway track points (frogs), crossings, switch components |
| Construction & Earth-Moving | Excavator bucket teeth, loader blades, bulldozer end bits, crusher parts for recycling |
| Material Processing | Pulverizer hammers, cage mill liners, screw conveyors, mixer blades for abrasive materials |
| Recycling Industry | Shredder hammers, anvils, and grates for metal, car, and waste shredding |
| Military & Security | Armor plating components (e.g., tank track links, hatches), protective barriers, safe/vault liners |
| Other Industrial | Pump housings for slurry, wear plates in chutes and hoppers, machinery gears subject to heavy shock |
Note: The effectiveness of manganese steel depends entirely on it being used in high-impact conditions that trigger its work-hardening behavior. In purely abrasive, low-impact settings, other materials like high-chrome iron may be more suitable.
5. How to Identify Manganese Steel Castings?
Spark Test: Grind with a grinding wheel; manganese steel sparks are dark red, with many dense branches and bright sparks at the tail. Different from the bright white sparks of ordinary steel.
Magnetic Test: Austenitic manganese steel is usually non-magnetic or weakly magnetic (note: the surface may become weakly magnetic after work hardening).
Hardness Change: New parts are relatively soft; used areas become exceptionally hard.
Safety Warnings:
- Cutting or welding manganese steel must be performed by professionals with strong ventilation. Manganese fumes are toxic at high temperatures, and long-term inhalation may cause "manganism," damaging the nervous system.
- During water toughening, the moment the high-temperature part enters the water, a large amount of steam is generated. Operators must be strictly protected to avoid burns.
6. Comparison with Other Wear-Resistant Materials
| Material Type | Initial Hardness | Toughness | Work Hardening Capacity | Suitable Working Conditions | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Manganese Steel | Relatively Low | Extremely High | Excellent | High Impact, High Stress Grinding | Medium |
| High Chromium Cast Iron | Extremely High | Low (Brittle) | Almost None | Low Impact, High Wear (Abrasive Wear) | Medium to High |
| Low Alloy Wear-Resistant Steel | Medium | Medium | Limited | Medium Impact, Sliding Wear | Relatively Low |
| Tungsten Carbide Hard Alloy | Extremely High | Extremely Low | None | Extreme Wear, Extremely Low Impact | Extremely High |
Simple Selection Principle: If the working conditions involve significant impact (e.g., pounding, crashing) and high-stress compression, high manganese steel is the first choice; if it is mainly sliding or low-stress wear (e.g., sand particle erosion), high chromium cast iron may be more suitable.
Conclusion
Manganese steel casting is an "ancient" technology invented over a century ago, but its clever principles and unique performance remain irreplaceable in many extreme working conditions today. It teaches us an important material science concept: The best material is not necessarily the hardest, but the one that best adapts to the environment and strengthens itself in the face of challenges.
Looking for premium metal casting services? Qianhao Foundry specializes in providing comprehensive metal casting solutions supported by deep industry expertise. We deliver high-quality cast components tailored to your project requirements, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Our domestic facilities maintain ready-to-ship precision-cast metal parts, offering customers timely access to quality casting solutions.