Melting steel for casting is a complex industrial process that requires extremely high temperatures, specialized equipment, and precise control over chemical composition. Unlike aluminum or cast iron, steel cannot be safely or consistently melted using basic furnaces or home setups. This article explains how steel is melted for casting, the equipment involved, and why professional steel foundries are essential for producing high-quality cast steel components. For a detailed explanation of what steel casting is, see our complete guide.
Why Steel Is Difficult to Melt for Casting
Steel has a high melting point, typically ranging from 1,370°C to 1,500°C (2,500°F–2,730°F) depending on its carbon content and alloy composition. This makes steel significantly more challenging to melt than other common casting metals.
Key challenges include:
- Extremely high and stable temperature requirements
- Precise alloy composition control
- Risk of oxidation, slag formation, and gas entrapment
- Safety hazards caused by molten steel at extreme temperatures
Because of these factors, steel casting is almost exclusively performed in industrial foundries using controlled environments.
What Equipment Is Used to Melt Steel for Casting?
Melting steel for casting requires industrial-grade furnaces capable of reaching and maintaining very high temperatures. Compared to other metals, steel casting vs aluminum casting involves stricter temperature and alloy control.
| Equipment Type | Description | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | Uses electromagnetic induction to heat and melt steel in a controlled environment. | Precise temperature control, clean melting process, accurate chemical composition control. |
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | Melts steel using high-voltage electric arcs generated between graphite electrodes. | Capable of melting large volumes, flexible raw material usage. |
| Crucible Furnace | Melts steel in a high-temperature refractory crucible using external heat sources. | Suitable for limited production and controlled melting. |
| Ladle Furnace (Secondary Refining) | Used after initial melting to further refine molten steel chemistry and temperature. | Improved metallurgical control and consistency. |
Step-by-Step Steel Melting Process for Casting (Industrial Overview)
In a professional steel foundry, the melting process follows a strictly controlled sequence.
1. Steel Charge Preparation
Steel charge preparation involves selecting and sorting steel scrap and raw materials based on the required grade. All materials are cleaned to remove oil, rust, moisture, and contaminants that could affect melt quality. The charge is accurately weighed and proportioned to ensure stable melting and minimize later alloy corrections, forming the basis for consistent chemical composition and reliable casting performance.
2. Furnace Heating
The prepared steel charge is loaded into an industrial furnace and heated gradually to its melting range of 1,370°C–1,500°C. Temperature and power input are carefully controlled to ensure uniform melting and avoid excessive oxidation. Stable furnace operation improves energy efficiency and prepares the molten steel for accurate chemical adjustment.
3. Alloy Adjustment
Once fully molten, alloying elements such as carbon, manganese, chromium, or nickel are added to achieve the target steel grade. Molten steel samples are analyzed, and adjustments are made to fine-tune composition. Precise alloy control ensures the final casting meets required strength, toughness, and performance standards.
4. Slag Removal
During melting, impurities rise to the surface and form slag. This slag is carefully removed to prevent inclusions and improve steel cleanliness. Proper slag control enhances molten steel fluidity, reduces casting defects, and contributes to better surface finish and overall casting quality.
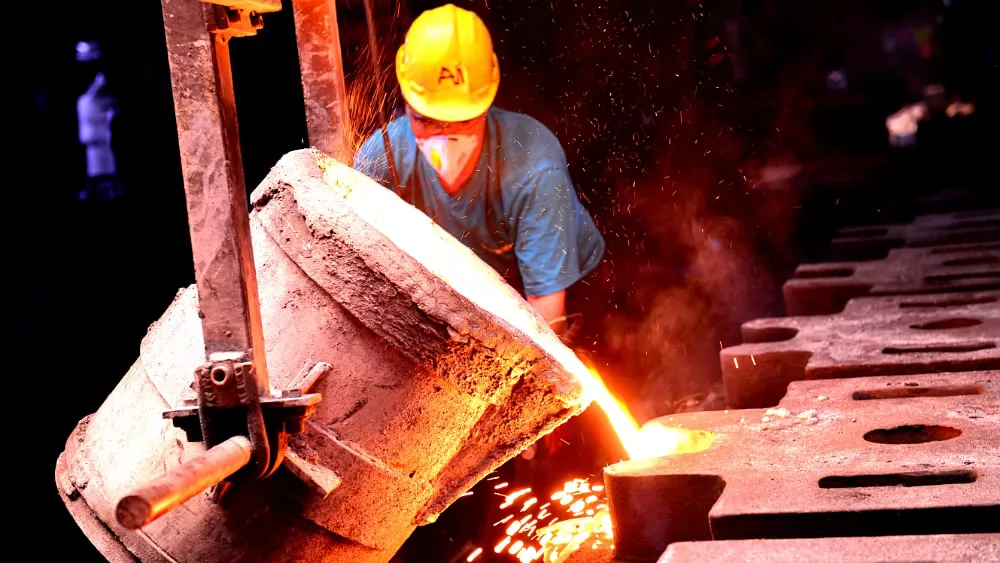
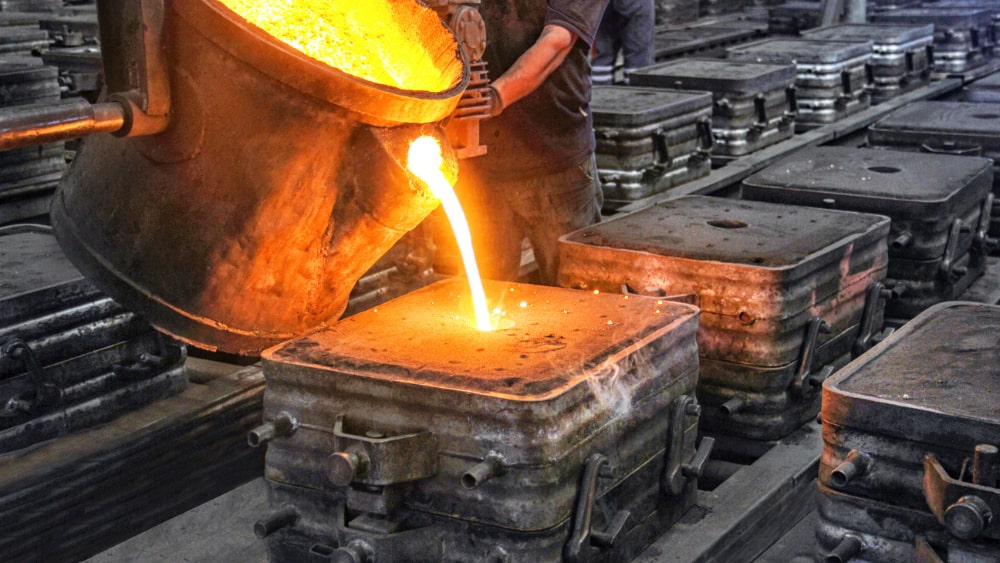
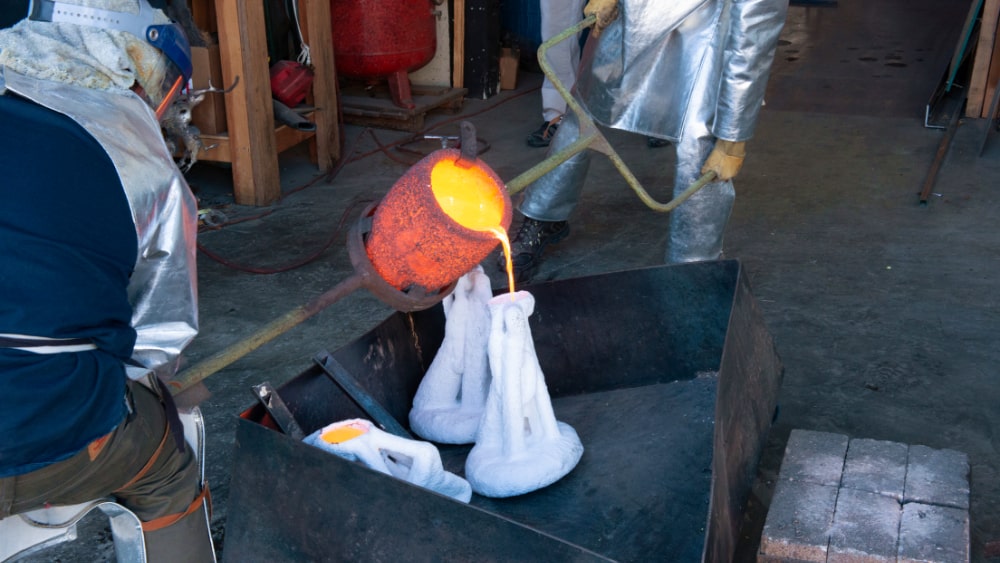
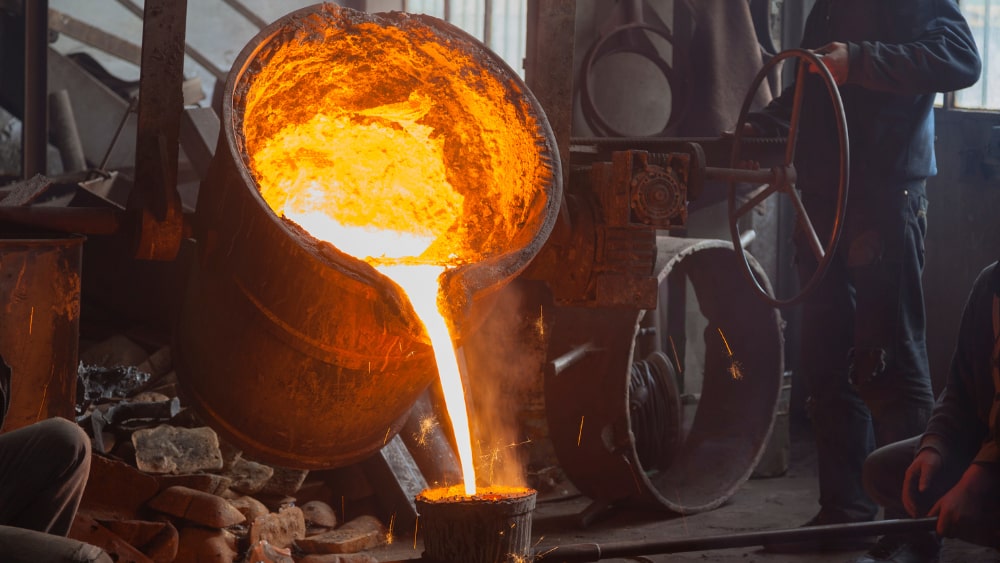
5. Pouring Molten Steel
Molten steel is transferred to ladles and poured into prepared molds at a controlled temperature. Proper pouring techniques ensure smooth flow, complete mold filling, and controlled shrinkage. Accurate timing and temperature control during pouring are critical to achieving sound, defect-free castings.
6. Cooling and Heat Treatment
After pouring, castings cool under controlled conditions to prevent cracking and internal stress. Once solidified, they are cleaned and may undergo heat treatment such as normalizing or tempering. These processes improve mechanical properties and ensure the steel casting meets application-specific requirements.
Safety Considerations When Melting Steel
Melting steel is inherently dangerous and requires strict safety measures:
- Specialized heat-resistant PPE
- Controlled pouring systems
- Explosion and splash protection
- Trained personnel and safety protocols
Even minor moisture or improper handling can cause violent reactions when molten steel is involved.
Can Steel Be Melted at Home for Casting?
No, steel cannot be safely melted at home.
Steel has a melting point of approximately 1,370°C to 1,500°C, which is far beyond the capability of common home furnaces or DIY equipment. Attempting to melt steel at home presents serious risks, including molten metal explosions, severe burns, and fire hazards. In addition, home setups cannot control chemical composition or remove impurities, resulting in poor-quality and unsafe castings. For alternative metal casting methods, see Lost Wax Casting Materials.
Looking for a Reliable Steel Casting Manufacturer?
If your project requires custom steel castings, working with an experienced manufacturer like Qianhao is the safest and most cost-effective solution. Qianhao delivers consistent product quality, precise metallurgical control, and reliable production timelines to meet demanding industrial standards.
- Machinery and equipment manufacturing
- Energy and power generation
- Construction and infrastructure
- Mining and heavy industry
Contact Qianhao today to discuss your application, technical specifications, and production requirements. Our engineering team is ready to support your project from concept to delivery.